by Anil Jalela | Aug 6, 2025 | Email
Google has introduced a new “Manage Subscriptions” feature in Gmail, giving users unprecedented control over their inboxes. With a centralized dashboard and a one-click unsubscribe option, people can now manage promotional emails with ease. For marketers, this means the days of relying on passive subscribers are over. The focus must shift toward delivering relevant, personalized, and genuinely valuable content.
While unsubscribe rates may increase in the short term, the long-term benefits are clear. Fewer spam complaints, stronger sender reputations, and cleaner subscriber lists will ultimately create a healthier email ecosystem built around engaged audiences.
How the Feature Works:-
With this update, Gmail now provides a Manage Subscriptions tab where users can see all their active email subscriptions in one place. These subscriptions are often organized by sending frequency, making it easy to spot who is sending the most.
From this dashboard, users can unsubscribe from any sender with a single click. They no longer need to scroll to the bottom of an email to find the unsubscribe link. The process of decluttering an inbox becomes much faster, giving users complete control over their email flow. Below is 3 main functionality of the Manage Subscriptions
Consolidated View
Gmail users have access to a central “Manage Subscriptions” tab that displays all active subscriptions, often sorted by frequency.
One-Click Unsubscribe
Users can unsubscribe from any sender instantly, without hunting for links inside the email footer.
Simplified Inbox Management
This dashboard makes it easier for users to declutter their inboxes and control the flow of promotional messages.
Impact on Email Marketers:-
Increased Unsubscribes
Marketers should expect unsubscribe rates to rise, especially in certain situations. People are more likely to opt out when content is irrelevant, when they receive too many emails in a short period, or when the value of the messages is low. Inactive subscribers who have not engaged for months are also more likely to leave once reminded of their subscription. Poor onboarding, where expectations about email frequency or content type are unclear, also drives unsubscribes.
Unsubscribe rates are expected to rise under specific conditions:
Irrelevant Content – Messages that don’t reflect subscriber interests.
High Frequency – Sending too many emails in a short time.
Low Value – Repetitive or generic promotions with little benefit.
Inactive Subscribers – People who haven’t engaged for months.
Unclear Expectations – Onboarding that fails to explain content type or frequency.
Focus on Quality Over Quantity
The new feature reinforces the need to send fewer but higher-quality emails. Subscribers will quickly abandon lists that rely on mass blasts with no personalization, campaigns that push constant promotions without value, or irrelevant offers sent without proper segmentation.
Subscribers are more likely to stay engaged when content meets their needs. Unsubscribes increase if marketers rely on:
Mass Blasts – One-size-fits-all messages with no personalization.
Lack of Segmentation – Sending irrelevant
Over-Promotion – Constant sales-driven emails with little educational or useful content.
Opportunity for List Hygiene
Although higher unsubscribes may feel discouraging, they lead to healthier lists. Removing inactive or disinterested subscribers ensures that only engaged people remain. Re-engagement campaigns can give dormant subscribers a chance to confirm their interest, while making the unsubscribe option easy prevents frustration and spam complaints.
The feature helps marketers maintain cleaner, more engaged lists. Best practices include:
Removing Inactives Regularly – Subscribers inactive for 6–12 months should be suppressed.
Re-engagement Campaigns – Offering dormant users the chance to confirm interest.
Easy Opt-Outs – Encouraging unsubscribes instead of risking spam complaints.
Improved Sender Reputation
A cleaner list means fewer spam complaints and better engagement signals such as opens and clicks. Internet service providers view this as a positive sign, improving deliverability over time. Respecting unsubscribes immediately also demonstrates compliance and builds trust with Gmail and other providers.
Deliverability improves when unsubscribes are respected:
Lower Spam Complaints – Fewer users resort to the “Report Spam” button.
Stronger Engagement Signals – Opens and clicks improve as only engaged users remain.
Compliance Signals – Honoring unsubscribes immediately builds trust with Gmail and other providers.
Emphasis on Customer-Centric Strategies
Marketers must put the subscriber first. This means using data to personalize content, offering preference centers where people can choose frequency or topics, and delivering messages that inform, entertain, or provide genuine help. Respecting consent and sending only to those who opted in is no longer optional — it is essential.
Success will rely on customer-first approaches such as:
Data-Driven Personalization – Tailoring content to behavior and preferences.
Preference Centers – Letting subscribers choose topics and frequency.
Balanced Content – Mixing promotions with helpful or educational information.
Respecting Consent – Emailing only those who have clearly opted in.
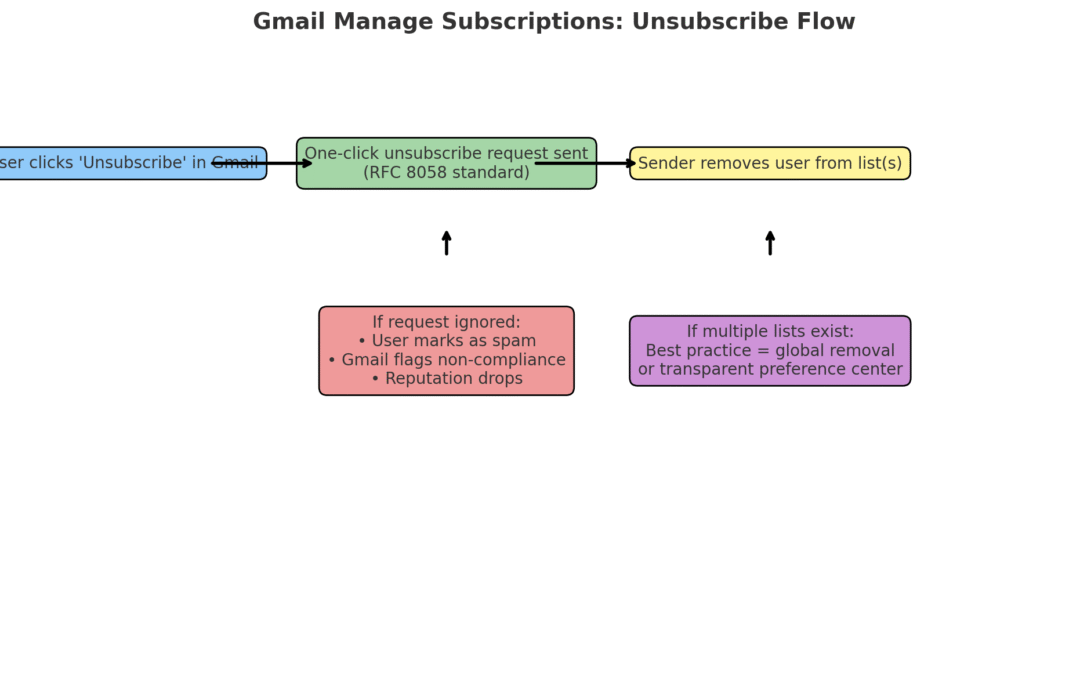
What Happens When Users Unsubscribe
When someone unsubscribes through Gmail’s Manage Subscriptions dashboard, a one-click unsubscribe request is sent using the industry standard defined in RFC 8058. This request is designed to remove the email address from all of the sender’s mailing lists.
If marketers ignore the unsubscribe request and continue sending, the consequences are serious. Users will likely mark those emails as spam, and Gmail may treat the sender as non-compliant. Over time, this damages deliverability, reduces inbox placement, and harms both domain and IP reputation.
Another challenge arises when the same email address is stored across multiple lists under the same sender. From the user’s perspective, unsubscribing once should stop all unwanted emails. If only one list is updated but others remain active, subscribers feel misled. This not only leads to frustration and spam reports but also increases legal risks under regulations such as CAN-SPAM and GDPR. The best practice is to apply unsubscribes globally across all lists tied to the same address, unless the user specifically manages preferences in a transparent preference center.
How Marketers Can Adapt
To succeed in this new environment, marketers must prioritize personalization and relevance. Messages should be crafted to match subscriber needs and interests. Audience segmentation is critical to ensure that the right people receive the right content at the right time.
Value must be at the heart of every campaign. Content should provide a clear benefit, whether that is education, entertainment, or practical help. Standard best practices such as double opt-in, careful data collection, and AI-driven personalization will continue to be important. Most importantly, marketers should honor unsubscribes immediately and treat one-click unsubscribes as a signal to stop all non-transactional emails.
Note:- To resubscribe, you must locate an email from the sender in your spam folder, then select the “Report not spam” option to move it back to your inbox, which can reactivate the subscription.
Final Thoughts
Google’s Manage Subscriptions feature is a reminder that the inbox belongs to the user. Marketers who rely on inflated lists or outdated tactics will see higher unsubscribes. But those who respect user choice, focus on relevance, and build trust will thrive.Unsubscribes are not the end of a relationship; they are the beginning of a cleaner, more engaged audience. The future of email marketing belongs to those who earn attention rather than demand it.
by Anil Jalela | Jun 5, 2025 | Email
Understanding the CAN-SPAM Act: A Practical Guide for Ethical Email Marketing. In a time where inboxes are flooded with daily messages, email continues to be one of the most effective and direct tools for business communication and digital marketing. However, this power must be used responsibly. If your organization is sending commercial emails to recipients in the United States, it is your legal duty to comply with the CAN-SPAM Act.
Failure to do so can result in substantial penalties, reputational harm, and long-term deliverability issues. At Nitwings, we support clients in building email strategies that go beyond performance,we ensure every message is legally compliant, ethical, and aligned with best practices in digital communication.
Below is a full-length guide to the CAN-SPAM Act, its key requirements, and actionable examples for applying them correctly.
What Is the CAN-SPAM Act?
The CAN-SPAM Act stands for Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing. It was enacted in 2003 to protect consumers from deceptive and unwanted commercial email messages(UCE). The law applies to all commercial email,not just bulk messages,and gives recipients the right to opt out of future emails. It also outlines rules for proper email identification and mandates transparency in content.
Under this law, each separate email that violates CAN-SPAM can result in fines of up to $51,744, making compliance not just a best practice, but a business imperative.
The law applies to:
=> Promotional email campaigns
=> Product announcements
=> Newsletter content with a commercial intent
=> Affiliate marketing communications
=> B2B marketing emails
The 7 Key Requirements of the CAN-SPAM Act (With Expanded Examples)
1. Do Not Use False or Misleading Header Information
The “From,” “To,” “Reply-To,” and domain routing details must clearly identify who is sending the email. These fields must not misrepresent the identity of the sender, nor should they try to obscure your brand’s true digital signature.
Compliant Example:
From: Nitwings Support <[email protected]>
This address matches the domain owned by Nitwings, giving the recipient confidence in the sender’s identity.
Non-Compliant Example:
From: Admin Team <[email protected]>
This appears generic, possibly deceptive, and doesn’t clearly indicate who the sender is or what business they represent.
Tip: Use a branded sending domain and make sure DNS records (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) are correctly configured to avoid being flagged as spoofed or fraudulent.
2. Do Not Use Deceptive Subject Lines
The subject line must truthfully represent the actual content of the message. Misleading subject lines are not only a breach of trust,they are explicitly prohibited under the CAN-SPAM Act.
Compliant Example:
Subject: “Get 25% Off Our Email Health Check Services – Offer Ends This Week”
This is promotional and makes it clear what the recipient can expect in the email body.
Non-Compliant Example:
Subject: “Your Account Is Suspended – Click to Reactivate”
If this email is just a marketing pitch for a product or service, this subject line is deceptive and could even be flagged as phishing.
Best Practice: Always aim for clarity over clickbait. Your reputation as a trustworthy sender is at stake with every subject line.
3. Identify the Message as an Advertisement
The recipient must be clearly informed that your email contains promotional content or commercial intent. There is flexibility in how this is disclosed, but the law requires that it be “clear and conspicuous.”
Compliant Example:
Footer note: “This email is an advertisement from Nitwings Technologies Pvt. Ltd. You are receiving this because you opted in or interacted with our services.”
Non-Compliant Example:
Email appears personal or transactional, with no disclosure that the content is promotional in nature.
Best Practice: Include this disclosure either at the top or in the footer. Make it clear but not obtrusive.
4. Include a Valid Physical Postal Address
All commercial emails must include a valid physical address.
This can be:
Your current business street address
A registered P.O. box with the U.S. Postal Service
A commercial mail receiving agency (CMRA) with appropriate registration
Compliant Example:
Nitwings Technologies Pvt. Ltd., 2nd Floor, ABC Tower, MG Road, Bengaluru – 560001, India
Non-Compliant Example:
No address listed, or using a fictitious address such as “123 Internet Blvd.”
Why It Matters: Including a real-world address helps establish credibility, and gives the recipient a way to contact you outside of email if necessary.
5. Provide a Clear Way to Opt Out of Future Emails
You must give recipients an easy, visible, and effective way to unsubscribe. The opt-out mechanism must be operational for at least 30 days after the email is sent.
Compliant Example:
Footer includes: “To stop receiving these updates, [click here to unsubscribe].”
Non-Compliant Example:
No unsubscribe link, or requiring the recipient to log in to an account to opt out.
Best Practice: Make unsubscribe links clear and easily clickable. Never hide them in small fonts or white text.
6. Honor Opt-Out Requests Promptly
Once a recipient unsubscribes, you must honor the request within 10 business days. Furthermore, you must not:
Charge a fee for unsubscribing
Require users to submit any additional information
Sell or transfer the unsubscribed email address (except for legal compliance purposes)
Compliant Example:
A subscriber opts out on June 1, and is fully removed from the list by June 5.
Non-Compliant Example:
Subscriber continues to receive emails weeks after opting out.
Tip: Automate your unsubscribe handling and integrate your CRM to instantly update suppression lists.
7. Monitor What Others Are Doing on Your Behalf
Even if a third party is managing your email campaigns, you remain legally responsible for what is being sent in your name.
Compliant Example:
You review and approve campaign content from agencies, and audit their compliance with unsubscribe requests and sender identity.
Non-Compliant Example:
You allow affiliates to send promotional emails using your brand without oversight.
Important: Always monitor affiliate or partner communications. Implement a compliance policy for all vendors.
Some more details
Quick Compliance Checklist Before You Hit “Send”
Use the following checklist to ensure every email is 100% CAN-SPAM compliant:
=> Include a working unsubscribe link that is easy to find.
=> Ensure opt-out requests are honored within 10 business days.
=> Display a valid, physical postal address in every email.
=> Use accurate “From” and “Reply-To” fields with branded domains.
=> Make sure the subject line truthfully reflects the content.
=> Clearly disclose the commercial nature of the message.
=> Regularly audit any third-party vendors or partners sending on your behalf.
Final Thoughts
The CAN-SPAM Act is not just a legal formality,it’s a foundational aspect of respectful, compliant digital marketing. Ethical email marketing builds trust, strengthens your sender reputation, and ensures long-term engagement with your audience.
At Nitwings, we are committed to helping brands not only reach the inbox but also stay compliant with all relevant regulations. From DNS setup to unsubscribe automation, our deliverability consultants are equipped to audit and optimize your campaigns from end to end.
Let’s deliver email the right way,smart, respectful.
by Anil Jalela | May 1, 2025 | Email
Microsoft has implement stricter email deliverability requirements for all bulk email senders from May 5, 2025. This move mirrors the sender policy enforcement already adopted by Gmail and Yahoo in 2024 and aims to strengthen email authentication, reduce spam, and protect inbox integrity across Outlook, Hotmail, Live, and MSN domains.
Key Requirements for Senders:
To maintain inbox placement and avoid delivery issues, bulk senders must comply with the following:
==>SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
Ensure a valid SPF record that authorizes your sending IPs and platforms (e.g., SendGrid, Amazon SES).
==>DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
Emails must be DKIM-signed to confirm authenticity and prevent tampering.
==>DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
A published DMARC policy is mandatory. At minimum: p=none, with proper alignment of the From domain with SPF or DKIM (ideally both).
==>Valid “From” and “Reply-To” Addresses
Both must point to real, functional inboxes that can accept replies. Microsoft explicitly discourages the use of dummy, blackholed, or unmonitored addresses like noreply@.
==>Local Parts (Before the @) to Avoid:
noreply@, admin@, root@, postmaster@, donotreply@, test@, spam@, bulk@, marketing@ (if not aligned), mailer@, info@ (if unmonitored), support@ (if fake)
==>Recommended Email Identities:
[email protected], news@, updates@, reply@, contact@, [email protected]
==>Applies To All Microsoft Consumer Domains:
Including but not limited to: hotmail.com, live.com, outlook.com, msn.com, and over 50 regional variants (hotmail.be, hotmail.ch, hotmail.co.id, hotmail.co.il, hotmail.co.jp, hotmail.co.kr, hotmail.com, hotmail.com.ar, hotmail.com.au, hotmail.com.br, hotmail.com.hk, hotmail.com.tr, hotmail.com.tw, hotmail.com.vn, hotmail.co.nz, hotmail.co.th, hotmail.co.uk, hotmail.co.za, hotmail.cz, hotmail.de, hotmail.dk, hotmail.es, hotmail.fi, hotmail.fr, hotmail.gr, hotmail.it, hotmail.my, hotmail.no, hotmail.ph, hotmail.rs, hotmail.se, hotmail.sg, live.at, live.be, live.ca, live.cl, live.cn, live.co.kr, live.com, live.com.ar, live.com.au, live.com.mx, live.com.my, live.com.ph, live.com.pt, live.com.sg, live.co.uk, live.co.za, live.de, live.dk, live.fr, live.hk, live.ie, live.in, live.it, live.jp, livemail.tw, live.nl, live.no, live.ru, live.se, microsoft, msn.cn, msn.com, outlook.com, windowslive.com)
==>What need to test:
audit your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configurations.
Review your sending addresses(from & Reply-To ) and ensure replies are accepted.
Avoid using placeholder, fake, or unmonitored inboxes.
| Authentication Volume Threshold |
5,000+ messages/day to Gmail, Yahoo doesn’t hold to a strict number but it is in the ballpark of 5000. |
5,000+ messages/day to Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, Live.com |
| SPF (Sender Policy Framework) |
Required |
Required |
| DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) |
Required |
Required |
| DMARC Policy |
Required. Minimum policy: p=none. Must align with SPF or DKIM. |
Required. Minimum policy: p=none. Must align with SPF or DKIM. |
| One-Click Unsubscribe (RFC 8058) |
Required. Bulk senders must include RFC 8058-compliant unsubscribe. |
Unsubscribe link required. RFC 8058 not required |
| List Unsubscribe Header |
Required. Must support List-Unsubscribe header with both mailto: and URL. |
Not explicitly required. |
| Spam Rate Threshold |
Required. Must stay below Gmail/Yahoo’s spam complaint thresholds of 0.3% |
No threshold defined, required to have clean lists and enforce best practices. Non compliant senders may experience negative action. |
| TLS (Transport Layer Security) |
Required. Emails must be sent over TLS. |
Not mentioned in Microsoft’s latest policy updates. |
| Valid HELO/EHLO |
Required. Must not use a dynamic IP or malformed hostname. |
Not explicitly required. |
| Forward/Proxy Detection |
Gmail penalizes misaligned forwarding or proxy behavior. |
No explicit guidance provided. |
| From: Header Alignment |
Must align with DKIM/DMARC domain. |
Recommended |
| Inactive/Invalid User Management |
Indirectly enforced through spam rate and complaint thresholds. |
Recommended |
| Functional Reply-To Address |
Recommended |
Recommended |
| Transparency (Subject lines, headers) |
Recommended to avoid misleading info. |
Recommended to avoid misleading info. |
| Timeline for Enforcement |
Full enforcement began February 2024. |
Enforcement begins May 5, 2025 with rejections at a later TBD. |
by Anil Jalela | Nov 20, 2024 | Email
Topics to Learn for Advanced Email Deliverability Techniques.
Mail Server Management: In-depth study of configuring and managing servers such as PowerMTA, Zimbra, Postfix, Strongmail, Qmail, and Exim.
Advanced Email Authentication: Best practices for implementing SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and BIMI, and managing DMARC reports for insights.
Bounce Management: Strategies for handling soft and hard bounces to improve email deliverability.
Spam Filters and Reputation Management: Tools like SpamCop, Watchguard, and Project Honey Pot to manage spam complaints and sender reputation.
Blacklist Management: Techniques for avoiding and recovering from IP or domain blacklisting.
Email Warm-up Strategies: Current methods for warming up domains, IPs, and email accounts to ensure high deliverability.
Content Optimization: Advanced techniques for avoiding spam filters, such as refining message headers, HTML coding, and keyword filtering.
ISP and ESP-Specific Expertise
Tools: Learn advanced features of ReturnPath, Google Postmaster Tools, Microsoft SNDS, 250Ok (now part of Validity), and Email On Acid.
ISP-Specific Compliance: Understanding the delivery mechanisms of Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook, and AOL.
ESP Tools: Hands-on experience with platforms like SendGrid, SES, Mailchimp, Benchmark, MailWizz, Interspire, Sendy, and MailTrain.
Marketing Automation & Analytics
Email Segmentation: Master advanced segmentation techniques based on user behavior, engagement, and demographics.
A/B Testing and Optimization: Learn how to conduct systematic testing for subject lines, email content, and CTAs to optimize performance.
Behavioral Triggers: Setting up automated workflows based on user interactions and lead scoring.
ROI-Driven Campaign Management: Using analytics to improve open rates, click rates, and conversions for campaign optimization.
Emerging Email Trends
AI and Machine Learning: Leverage AI for personalized email campaigns, predictive deliverability analysis, and insights into user behavior.
Zero-Party Data Utilization: Use voluntarily shared data from users to enhance segmentation and personalization strategies.
Dark Mode Optimization: Designing email templates that are optimized for dark mode compatibility across various devices.
AMP for Email: Explore dynamic content delivery within emails using AMP.
Domain Alignment and BIMI: Strengthen brand trust by ensuring domain alignment and implementing BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification).
Lead Generation and Outreach
LinkedIn Outreach: Creating targeted LinkedIn campaigns, advanced research using Sales Navigator, and automating LinkedIn lead generation.
Data Collection: Online research for lead sourcing and utilizing email validation and enrichment tools like Snovio and SalesQL.
Social Media Outreach: Best practices for DM campaigns on platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter.
eCommerce and Advanced Campaigns
eCommerce Platforms: Master the integration of Klaviyo with Shopify, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce, and crafting pre-purchase, cart abandonment, and post-purchase flows.
Segmentation and Personalization: Learn advanced segmentation techniques and how to personalize campaigns based on user behavior for better targeting.
Email Marketing Tools
Tool Mastery: Deep-dive into tools like Gmass, Sendinblue, Mailchimp, Sendgrid, Mailer Lite, Mailer Cloud, Blue Core, and Mailtester and compare their features and use cases for email campaigns.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Email Marketing Laws: Understand and comply with global email marketing laws like GDPR, CAN-SPAM, and CCPA to ensure legal compliance in all campaigns.
Additional Tools and Certifications
Tool Certifications:
HubSpot Email Marketing Certification
Google Analytics for Marketers
Klaviyo Email Marketing Certification
Salesforce Pardot Specialist
Marketo Certified Expert
Deliverability & Anti-Spam Certifications:
Certified by ReturnPath (Validity)
Certified Email Marketing Professional (CEMP)
M3AAWG Training on Anti-Abuse & Deliverability Practices
Cloud Platforms:
AWS SES and Pinpoint
Google Cloud (Cloud DNS for email-related configurations)
Microsoft Azure (SMTP and transactional email setups)
Technical Skills
DNS Management: Master advanced configurations for SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and MX records.
Postfix and PowerMTA Tuning: Optimize performance and queue management.
Python for Email Analytics: Use Python for data analysis, automation scripts, and email deliverability audits.
Soft Skills
Email Copywriting: Learn to craft compelling, conversion-driven email content.
Cross-Channel Strategy: Integrate email marketing with LinkedIn, SMS, and other outreach channels for comprehensive campaigns.
Recommended Tools to Master
Deliverability Monitoring Tools:
250Ok (Validity)
GlockApps
Postmaster by Gmail
EmailConsul
Warmbox
Anti-Spam Monitoring & Reputation Tools:
MXToolbox
Talos Intelligence
Barracuda Central
Marketing Automation:
ActiveCampaign
HubSpot
Autopilot
Testing & Preview Tools:
Litmus
Email on Acid
Lead Generation & Outreach Tools:
Instantly
Lemlist
Apollo.io
Woodpecker.co
Data Tools:
Hunter.io
Snov.io
Clearbit
by Anil Jalela | Mar 30, 2024 | Email
As an email marketer, reaching his audience effectively is essential for the success of your campaigns. In today’s online world, many people use temporary email addresses called disposable email domains. This can be both good and bad for email marketers. Understanding how disposable email domains impact your email marketing efforts is crucial for optimizing engagement and maximizing results.
What are Disposable Email Domains?
Disposable email domains are temporary email addresses created for short-term use. Users often employ these addresses to sign up for online services, newsletters, or forums without giving out their main email address. Popular disposable email services include 10minutemail.com, Guerrilla Mail, and Temp Mail.
Challenges:-
Low Engagement Rates: Emails sent to disposable addresses may have lower open and click-through rates since users often use them for temporary purposes and may not engage with the content.
Spam Filtering: Many disposable email domains are flagged by spam filters, leading to your emails being automatically routed to the spam folder or rejected altogether.
Data Quality Concerns: Since disposable email addresses are temporary, maintaining accurate subscriber data becomes challenging, impacting the quality of your email list.
Deliverability Issues: Email service providers may view emails sent to disposable addresses as suspicious, affecting deliverability rates and sender reputation.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges:-
Segmentation: Segment your email list to identify and exclude disposable email addresses. Focus your efforts on engaging with subscribers who are more likely to interact with your content.
Email Verification: Implement email verification processes during the signup phase to detect and block disposable email addresses. This ensures that your list comprises genuine subscribers who are interested in your content.
Content Personalization: Tailor your email content to resonate with your audience’s interests and preferences. Personalized emails are more likely to capture the attention of subscribers, regardless of the email address type.
Optimize Deliverability: Monitor your email deliverability metrics closely and address any issues promptly. Utilize best practices for email authentication, such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, to enhance deliverability and inbox placement.
Incentivize Engagement: Offer incentives or exclusive content to encourage subscribers to use their primary email addresses rather than disposable ones. This fosters a more meaningful connection with your audience and increases the likelihood of sustained engagement.
block and verification:-
block into PowerMTA:-
domain-macro Disposable_dom nitwings.com, 0-00.usa.cc, 001.igg.biz
<domain $Disposable_dom>
type discard
discard-as-bounce yes
</domain>
block into Postfix:-
add the line in the Postfix’s “/etc/postfix/main.cf”.
transport_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/transport
Way one:- only send an email for Yahoo and Gmail all other domains are discarded
write /etc/postfix/transport
gmail.com:
yahoo.com:
* discard:
Way two:- only discard specific domains and all others are allowed.
create /etc/postfix/transport
nitwings.com discard:
blackpost.net discard:
Where to get Disposable:-
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/iocium/download.throwaway.cloud/main/list.txt
“https://raw.githubusercontent.com/andreis/disposable-email-domains/master/domains.json”
“https://github.com/ivolo/disposable-email-domains/blob/master/wildcard.json”
You can use open.kickbox.com free API to write automation and find out whether the domain is disposable or not.
“https://open.kickbox.com/v1/disposable/yopmail.com”
Small Providers need to block disposable domains because spam filter providers use unused disposable boxes as traps and generate high spam complements. Also, it is included in phishing and suspicious activity.
