Jenkins:-
→ Jenkins is an Open-Source project Written in Java that runs on Windows, macOS, and Other Unix-like Operating Systems. It is free, Community Supported, and might be your first-choice tool for CI.
→ Jenkins automates the entire Software development life Cycle
→ Jenkins was Originally developed by Sun Microsystem in 2004 under the name Hudson.
→ The project was later named Jenkins when Oracle bought Microsystems.
→ It Can run on any major platform without any Compatibilities issues.
→ Whenever developers Write Code, we integrate all that Code of all developers at that point in time and we build, test, and deliver/Deploy to the client. This process is called CI/CD ..
→ Jenkins helps us to achieve fast development.
→ Because of CI, Now bugs will be reported fast and get rectified fast So the entire Software development happens fast.
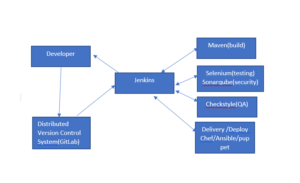
Workflow of Jenkins:-
→ We Can attach git, Maven, Selenium, Sonarqube, and Artifactory plugins to Jenkins.
→ Once developers put Code in GitHub, – Jenkins pulls that Code & sends to Maven for build
→ Once the build is done Jenkins pulls that Code and sends it to Selenium for testing.
→ Once testing is done, then Jenkins will pull that Code and Send it to artifactory (archive) as per requirement and so on.
→ We Can also deploy codes with Jenkins.
Build means=( compile, code review, unit testing, Integration testing, packaging[tar,jar,exe] )
Advantages of Jenkins: –
→ It has lots of plug-ins available
→ You Can Write your own plug-in.
→ You Can use Community Plug-in.
→ Jenkins is not just a tool. It is a framework i.e.: – You Can do whatever you want All you need is plug-ins.
→ We Can attach Slaves (nodes) to Jenkins master. It instructs others (slaves) to do Job. If slaves are not available Jenkins itself does the job.
→ Jenkins also behaves as a crone Server Replacement. i.e.: – Can do the scheduled task.
→ It Can Create Labels
| 1 | yum install yum install fontconfig java-11-openjdk.x86_64 | install java |
| 2 | alternatives –config java | the set version of java |
| 3 | cp /etc/profile /etc/profile_backup | backup profile |
| 4 | echo ‘export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/ /usr/lib/jvm/jre_11_openjdk’ |tee -a /etc/profile | export java development kit home |
| 5 | echo ‘export JRE_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/jre’ | tee -a /etc/profile | export JVM home |
| 6 | source /etc/profile | export configurations in the current system environment |
| 7 | wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo | Download the stable repo for yum |
| 8 | rpm –import https://pkg.jenkins.io/redhat-stable/jenkins.io.key | Import key for package signature verification |
| 9 | yum install jenkins | Install Jenkins |
| 10 | systemctl start jenkins.service | Start Jenkins service |
| 11 | systemctl enable jenkins.service | Enable Jenkins service |
what needs to learn in Jenkins?
Introduction to Jenkins
Introduction to Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration vs Continuous Delivery
Jenkins Overview
Characteristics and features
Architecture
Concepts and Terms
Benefits and Limitations
Installation and Configuration
Jenkins Installation and Configuration
Plug-ins Overview
Integration with Git
Integration with Maven
Integration with Java
Installing plugins
Setting up Build Jobs
Jenkins Dashboard
Create the first job
Running the first job
Manage jobs – failing, disable, update and delete
Pipeline with Jenkinsfile
Freestyle Project Configuration
Git Hooks and Other Build Triggers
Workspace Environment Variables
Parameterized Projects
UpstreamDownstream Projects and the Parameterized Trigger Plugin
Build a Java application with Maven using Jenkins
Continuous Delivery Pipeline
Publishing Build Artifacts
Deployment Plug-in setup and configuration
Auto Deployment of build artifacts into the target server
Deploy a Java application with Maven using Jenkins
Executing selenium Functional Testing with deployment
Management, Security and Best Practices
Managing and Monitoring Jenkins Server
Scaling Jenkins
Securing Jenkins
Adding Linux Node and executing job on it
Adding windows node and executing job on it
Configuring access control on Jenkins
Configuring role-based access control
Jenkins logs
Management
Credentials in Jenkins
Best Practices
Jenkins Pipeline
Writing Jenkins Pipeline file for java application build and deployment
Storing Jenkins in git and configuring webhook
Difference between declarative and scripted pipeline
Specify an agent in the pipeline
Parameters in Pipeline
Schedule build in the pipeline
Webhook in pipeline
Approval in pipeline
Approval with timeout in the pipeline
Variables in pipeline
Email notification in the pipeline
Post-build action in the pipeline
Parallel stages in the pipeline
Condition in pipeline
Selenium Functional Testing in the pipeline
